Interaction Lifecycle
Interactions are used to change the state of contracts and invoke computations defined in the contract's source code. However, before any of that can happen, the interaction must go through a lifecycle, which is not such a simple process.
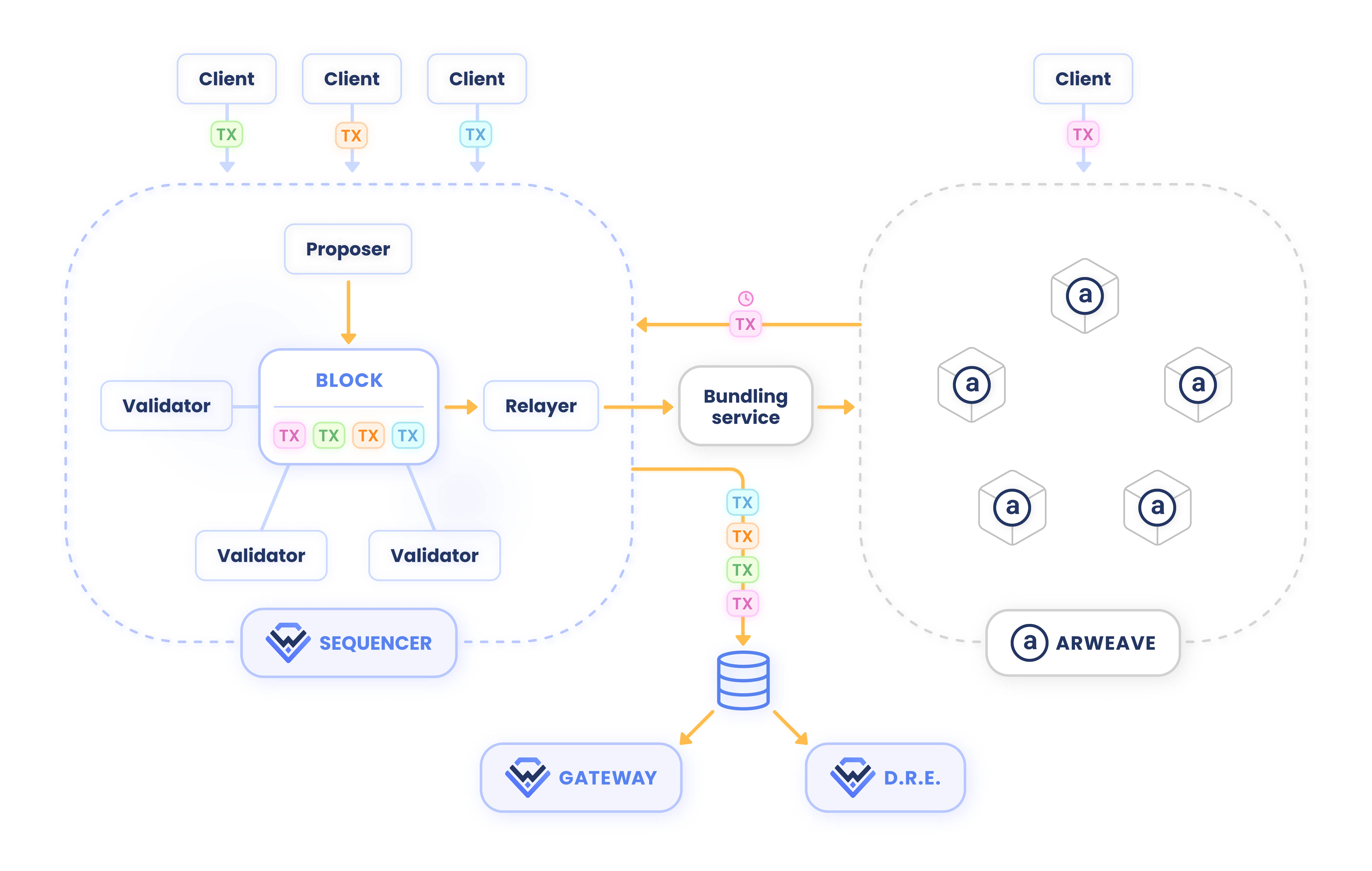
In brief, the lifecycle of an interaction begins when it is created and sent by the Warp SDK. The interaction is then received by the Warp Sequencer, which establishes order relative to other interactions. The process of ordering involves generating keys on which the interactions are sorted, as well as generating random values in case the contract needs them. The interaction is then sent to its final destination, Arweave.
Meanwhile, through notifications dispatched by the sequencer, interactions are stored in a database used by the Warp Gateway to construct its indexes. The gateway can then be leveraged by SDK or Warp D.R.E. nodes to retrieve a list of interactions for a contract, enabling the evaluation of the contract's state.
The path for interactions sent by the client directly to Arweave is slightly different. Sequencer nodes download these interactions to insert them into the linear order along with interactions that are sent directly to the sequencer. Due to the characteristics of the Arweave blockchain, these interactions must be downloaded with a certain delay (hence the clock icon in the diagram below). For this type of interaction, the sequencer also sends data to Arweave, but only information related to the ordering of the interactions and random values.
The gateway receives a common list of interactions regardless of whether they were sent to the sequencer or to Arweave.
The stages of the interaction lifecycle will be described in detail in the following sections.